AMD’s Q2 2025 Triumph: Ryzen & EPYC Seize Control of the CPU Market
For years, the CPU landscape felt like an unyielding monolith, but AMD’s relentless innovation has irrevocably reshaped it. Today, JoltGamer is diving deep into the seismic shifts revealed by the Q2 2025 market share report, which paints a vivid picture of AMD’s accelerating dominance. With record revenue share across key segments, particularly in the lucrative desktop and server markets, AMD’s Ryzen and EPYC processors aren’t just gaining ground—they’re seizing control, signaling a new era for high-performance computing. Let’s peel back the layers and understand the numbers that define this triumph.
The Ascent Unveiled: AMD’s Overall Market Share Gains
Overall x86 CPU Market Share – Q2 2025
Record High (YoY Gain) – Across all major categories
2:1 Sales Ratio – Narrowing from 9:1 previously
Notes: AMD achieved record revenue share with significant year-over-year gains, driven by high-end product sales. Intel maintains overall volume leadership, but the sales ratio has narrowed significantly from 9:1 to 2:1 in AMD’s favor.
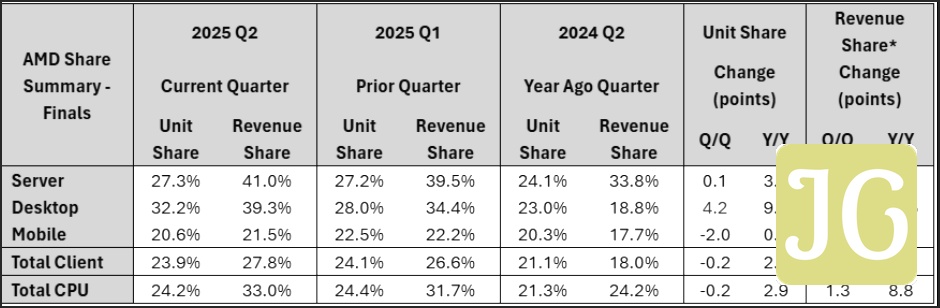
The Q2 2025 Mercury Research data paints a clear picture: AMD has achieved truly spectacular year-over-year gains, setting new revenue share records across virtually every major CPU category. This isn’t merely incremental growth; it’s a testament to the strong uptake of their higher-end products, particularly in the lucrative desktop and server segments where AMD is consistently capturing a larger slice of premium sales. While Intel still holds the overall volume leadership, shipping more processors across the board, the competitive landscape has fundamentally shifted. The once-staggering 9:1 sales ratio in Intel’s favor just a few years ago has now narrowed to a far more competitive 2:1, underscoring AMD’s strategic inroads and the market’s evolving preferences for performance and value.
Desktop Dominance: Ryzen’s Reign
Desktop CPU Market Share – Q2 2025
Notes: AMD’s desktop CPU unit share reached a new high of 32.2%, with a significant 9.2% year-over-year gain. Revenue share surged to 39.3%. Intel’s unit share declined QoQ and YoY to 67.8%.
AMD’s desktop CPU market share has indeed hit a new high, soaring to a remarkable 32.2% unit share and an even more impressive 39.3% revenue share in Q2 2025. This surge is directly attributable to the resounding success of the Ryzen 9000-series processors, which have captivated both consumer and commercial markets, especially within the critical enthusiast and high-performance segments. The impact of AMD’s innovative 2nd Gen 3D V-Cache™ technology, found in its X3D and flagship 9000X3D Series, cannot be overstated; its massive gaming performance boost, paired with advanced cores, has made Ryzen the go-to choice for serious gamers. Furthermore, AMD’s commitment to the Socket AM5 platform, promising years of future support with high-speed DDR5 and PCIe 5.0, provides a compelling long-term value proposition that resonates with users. While Intel still outsells AMD 2:1 in desktop CPUs, this represents a significant narrowing from previous years, clearly demonstrating that AMD is rapidly eroding Intel’s once-unassailable lead in the desktop space by delivering superior performance, features, and platform longevity.

Server Conquest: EPYC’s Unstoppable Momentum
Server CPU Market Share – Q2 2025
Notes: AMD’s server CPU unit share reached 27.3% with steady QoQ gains and strong YoY growth. Revenue share surged to 41%. Intel maintains unit share leadership but is losing ground in premium segments.
The data center segment continues to be a formidable growth engine for AMD, with its EPYC processors maintaining their unstoppable momentum. In Q2 2025, AMD’s server CPU unit share reached 27.3%, a steady, albeit slightly slower, sequential gain that builds on robust year-over-year performance. The relentless demand for EPYC processors is driven by their superior performance, exceptional efficiency, and a compelling total cost of ownership that resonates deeply with cloud providers and enterprises alike. While Intel still holds the majority of server CPU shipments, outselling AMD 7:3, the more telling metric is revenue share. AMD’s server CPU revenue share surged to an impressive 41% in Q2, a significant 7.2% year-over-year jump that almost matches its desktop revenue share. This indicates that EPYC is not just gaining volume but is increasingly dominating the highly profitable, premium end of the server market, a segment where Intel is visibly struggling to compete.

Intel’s Shifting Sands: Losing the Premium Edge
Premium Market Battleground: AMD vs. Intel
AMD’s Premium Strategy
-
Focus:
Strategic emphasis on high-end, enthusiast, and performance segments across desktop and server. -
Desktop Success:
Ryzen 9000-series, X3D, and AM5 platform driving significant gains in premium desktop sales. -
Server Success:
EPYC processors dominating the premium server market with superior performance and TCO.
Intel’s Premium Challenges
-
High-End Sales:
Lower-than-usual sales of premium desktop processors. -
Enthusiast Reception:
Core Ultra 200-series proving unpopular with enthusiasts, failing to capture mindshare. -
Server Market:
Largely lost the premium server market, struggling to broadly compete with AMD’s high-end EPYC offerings.
Intel’s grip on the CPU market, particularly in its most lucrative higher-end segments, is demonstrably loosening. The erosion of their market share in premium desktop and server categories is a stark indicator of shifting tides. Sales of Intel’s high-end processors are lower than what the market has come to expect, and the Core Ultra 200-series has largely failed to resonate with the enthusiast community, further highlighting their struggle to maintain a competitive edge where it counts most. This strategic misstep contrasts sharply with AMD’s calculated focus on these high-margin segments. Adding another layer to Intel’s challenges is AMD’s strategic decision to exit the low-margin Chrome device market over a year ago. While this move might have subtly impacted AMD’s overall mobile unit share, it has a more significant, albeit indirect, effect on Intel. By continuing its substantial presence in the high-volume, low-profitability Chrome system market—where devices often sell for $200-$300 in large educational deals—Intel’s overall average selling price is inevitably dragged down, making its financial performance appear less robust in comparison to AMD’s premium-focused revenue gains.

The Strategic Playbook: How AMD Did It
- Revolutionary Zen Architecture: The foundation of AMD’s comeback, Zen delivered unprecedented performance, efficiency, and scalability, providing a potent alternative to incumbent designs.
- Pioneering Chiplet Technology: Introduced with Zen 2, this modular approach extended Moore’s Law, enabling higher core counts, improved yields, and cost-effective manufacturing, giving AMD a significant design advantage.
- Future-Proof AM5 Platform: AMD’s commitment to the AM5 socket, integrating DDR5 memory and PCIe 5.0, ensures long-term upgradeability and value for consumers, fostering loyalty.
- Game-Changing 3D V-Cache: A direct boon for gamers, 3D V-Cache technology delivers massive performance boosts, particularly in gaming, making Ryzen X3D processors highly sought after.
- Aggressive AI Integration: From Ryzen AI in client processors to the powerful Instinct MI300 series and the XDNA architecture for data centers, AMD is strategically embedding AI capabilities across its entire product stack.
- Critical Strategic Partnerships: Key alliances with TSMC for leading-edge manufacturing, hyperscalers like Microsoft Azure and AWS for EPYC adoption, and exclusive APU supply for PlayStation and Xbox consoles have solidified AMD’s market position and revenue streams.
AMD’s Turnaround: A Decade of Innovation
Dr. Lisa Su Appointed CEO
Marked the beginning of AMD’s strategic overhaul, prioritizing innovation and R&D amidst financial struggles.
Zen CPU Architecture Unveiled
The launch of Ryzen processors, based on the Zen architecture, initiated AMD’s resurgence, offering competitive performance and core counts.
Zen 2 & Chiplet Technology
Pioneered chiplet design at scale, enabling higher core counts, improved efficiency, and cementing AMD’s leadership in multi-core performance.
Zen 3 Architecture
Further refined performance and efficiency, allowing Ryzen to consistently outperform Intel in many markets.
Xilinx Acquisition
A $35 billion strategic move that significantly bolstered AMD’s presence in AI, machine learning, and adaptive computing.
Instinct MI300 Launch
Introduced the world’s first data center APU, positioning AMD as a direct competitor in the high-growth AI accelerator market.
Zen 5 Architecture Plans
Outlined plans for the next-generation CPU core, designed for leadership performance and efficiency, with strong AI/ML optimizations.
Q2 Market Dominance
Achieved record revenue share and significant market gains in desktop and server segments, solidifying its position as a high-performance computing leader.
The Fabless Advantage: A Strategic Masterstroke
A critical, often understated, element of AMD’s resurgence is its ‘fabless’ manufacturing strategy. Unlike Intel, which historically relied on its own internal fabrication plants, AMD made the pivotal decision to divest its manufacturing arm into GlobalFoundries in 2009. This move allowed AMD to focus solely on chip design, leveraging cutting-edge external fabs like TSMC. This strategic flexibility proved to be a game-changer. While Intel struggled with delays and challenges in transitioning to smaller process nodes (like 10nm and 7nm), AMD was able to rapidly adopt TSMC’s advanced 7nm process for its Zen 2 architecture, delivering superior performance and efficiency sooner. This agility in manufacturing, contrasted with Intel’s internal struggles and complacency, provided AMD with a crucial competitive edge, enabling rapid innovation and accelerating its market share gains across the board.
Financial Fortitude: Q2 2025 Earnings Breakdown
Q2 2025 Earnings Breakdown
| Metric | Q2 2025 Result | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $7.7 billion | Record high, +32% YoY |
| Reported Gross Margin | 43% | Impacted by write-down |
| Adjusted Gross Margin | 54% | Excluding inventory write-down |
| Operating Expenses | $2.4 billion | +32% YoY |
| Operating Income | $897 million | 12% operating margin |
| Free Cash Flow | Over $1 billion | Strong cash generation |
| Inventory Write-down | $800 million | Due to US export controls (MI308 to China) |
| Data Center Segment Operating Loss | $155 million | Impacted by write-down |
| Cash & Equivalents | $5.9 billion | Solid financial position |
| Long-term Debt | $3.2 billion | Manageable debt levels |
| Share Repurchases (Q2) | $478 million | Part of $1.2 billion in H1 2025 |
AMD’s Q2 2025 financial results present a nuanced, yet overwhelmingly positive, picture of a company executing its strategy with precision. While the company achieved a record revenue of $7.7 billion—a staggering 32% year-over-year increase driven by the stellar performance of Ryzen and EPYC processors—it did report an earnings per share (EPS) miss. This miss, however, is largely contextualized by a significant, one-time $800 million inventory write-down. This write-down was directly attributed to US export controls that impacted sales of the MI308, AMD’s powerful AI accelerator, to China. Such a substantial charge naturally reduced the reported gross margin to 43%, but when this charge is excluded, the underlying gross margin stands at a much healthier 54%. The write-down also contributed to the Data Center segment’s operating loss of $155 million, a temporary blip in what is otherwise a rapidly expanding sector for AMD. On the positive side, segmental growth was truly exceptional: the Client and Gaming division surged an incredible 69% year-over-year to $3.6 billion, fueled by record client CPU sales and robust gaming product demand. The Data Center segment, even with the write-down, still grew a substantial 14% year-over-year to $3.2 billion, underscoring the relentless demand for EPYC processors in critical cloud and enterprise workloads.
The Fandom Pulse: Confidence Meets Pragmatism
“There still so much more Unit Share it seems on the table, but AMD has stayed away from low end, low margin targets thus far. What I think can and likely is happening, AMD’s last gen offering are able to still best Intels mid and low end offering and thus is eating into Intels core foundations, both client and server.”
The JoltGamer community, ever perceptive, reflects a blend of confident optimism and pragmatic, forward-looking discussion regarding AMD’s trajectory. As the representative quote highlights, there’s a clear understanding that AMD has strategically avoided the low-end, low-margin segments to focus on premium, high-value offerings. However, the insight that AMD’s previous generation technologies are now competitively challenging Intel’s mid and low-end offerings is a potent one. This clever leverage of cost-effective, yet still powerful, older architectures allows AMD to eat into Intel’s foundational market share in both client and server spaces without diluting its brand or profitability with direct low-end competition. The ongoing discussion within the community revolves around how AMD can best allocate its resources to maintain this profitable high-end focus while strategically expanding into broader market segments for sustainable future growth, perhaps even leveraging these mature, cost-optimized products for deeper penetration into the mainstream and budget markets when the time is right.
Looking Ahead: AI, Growth, and Market Uncertainties
Looking ahead to Q3 2025, AMD’s outlook remains confidently positive, despite navigating a complex geopolitical and economic landscape. The company projects revenue to be approximately $8.7 billion, with a margin of plus or minus $300 million, and anticipates a healthy gross margin of around 54%. This guidance is notably pragmatic, explicitly excluding any revenue from MI308 shipments to China, as license applications for these crucial AI accelerators remain under review due to ongoing US export controls. Despite this constraint, the demand for AMD’s AI products is described as “robust,” positioning the company for “significant” future growth in this burgeoning market. While AMD doesn’t believe there was significant pull-forward in its Q2 Client business results, it does expect continued growth in this segment for the second half of the year, albeit at a pace less than seasonally typical due to prevailing market uncertainties. This measured optimism reflects a company that understands its strengths and is strategically navigating challenges.
The Road Paved by Innovation
AMD’s Q2 2025 performance is more than just a quarterly report; it’s a testament to a decade-long strategic transformation. The company stands today in an exceptionally strong market position, driven by a relentless commitment to innovation embodied in its groundbreaking Zen architecture, pioneering chiplet technology, and aggressive integration of AI across its product lines. Strategic partnerships with key industry players, from leading-edge fabs like TSMC to cloud giants and console manufacturers, have further solidified its foundation. By effectively positioning its products in the high-performance and enthusiast segments, AMD has not only reclaimed significant market share but has fundamentally reshaped the competitive landscape. As we look to the future, it’s clear that AMD is not merely participating in the high-performance computing and gaming markets—it’s actively defining their trajectory, promising continued excitement and innovation for years to come.